How to Automate Procurement with No-Code Tools
Product
11 mins
Dec 22, 2025

Khyati Mehra
Procurement automation leverages technology to systematize and accelerate the high-volume, repetitive tasks inherent in the purchasing lifecycle, from requisition to final payment. It is not merely an efficiency tool but a strategic imperative for modern enterprises. Implementing robust automation is the key to material cost reduction, enhanced data accuracy, and a durable competitive advantage.
This paradigm shift elevates procurement from a reactive, cost-centric function to a proactive, value-driven strategic partner within the organization.
Why Automation in Procurement Is No Longer Optional
Procurement teams are operating under unprecedented pressure. They must contend with volatile global markets, persistent supply chain disruptions, inflationary pressures, and stringent regulatory compliance—all while being expected to drive strategic value. Attempting to manage these complexities with manual, paper-based systems is not just inefficient; it constitutes a significant operational and financial risk.
Manual procurement is inherently slow and error-prone. Processes like purchase requisition routing, invoice matching and approval, and supplier data maintenance consume thousands of hours that could be reallocated to strategic activities. This administrative burden creates process bottlenecks, delays critical payments, and obscures visibility into enterprise-wide spend.
Without automation, teams remain mired in a reactive cycle, perpetually addressing tactical fires instead of architecting strategic advantages.

The Strategic Imperative for Change
Deploying automation in procurement is the definitive response to these systemic challenges. Digitizing the procure-to-pay lifecycle unlocks benefits that transcend mere transactional speed.
The core objective of automation is to liberate highly skilled professionals from low-value, repetitive tasks. This reallocation of human capital enables them to focus on mission-critical functions: cultivating strategic supplier relationships, negotiating complex contracts, and performing deep data analysis to uncover savings opportunities.
Market data underscores this transition. The procurement software market is projected to reach $9.5 billion by 2028, signaling its escalating importance. This growth is driven by a 10.6% increase in global procurement workloads amid talent shortages, positioning automation as an essential enabler of scalability. You can explore further procurement statistics to grasp the full market context.
Ultimately, automation establishes the foundation for a more agile, resilient, and intelligent procurement function, empowering organizations to:
Improve Spend Visibility: Gain a real-time, consolidated view of organizational spend, enabling data-driven decision-making.
Strengthen Compliance: Embed purchasing policies into automated workflows, mitigating rogue spending and reducing regulatory risk.
Enhance Supplier Collaboration: Streamline communication and accelerate payment cycles, fostering stronger, more strategic supplier partnerships.
The Technologies Powering Smart Procurement
To fully grasp the transformative potential of automation in procurement, it is crucial to understand the underlying technologies. These are not speculative concepts but proven tools that synergize to create an intelligent, responsive procurement ecosystem. They function as a cohesive system, each component executing a specialized role to optimize the entire procure-to-pay lifecycle.
The strategic investment in this area is significant. Global spending on digital supply chain solutions is forecast to exceed $19 billion annually by 2025. This reflects a fundamental strategic pivot: Gartner predicts that by the end of 2025, 50% of large global enterprises will leverage AI, advanced analytics, and IoT in their supply chain operations.
Let's dissect the core technologies and their specific applications within the procurement domain.
Key Technologies in Procurement Automation
Technology | Core Function | Primary Use Case in Procurement | Strategic Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) | Mimics human actions for repetitive, rules-based tasks. | Data entry, three-way invoice matching, purchase order generation. | Frees human capital from manual processes, reduces errors, accelerates cycle times. |
Artificial Intelligence (AI) & Machine Learning (ML) | Analyzes data, identifies patterns, and makes predictions or recommendations. | Predictive spend analysis, supplier risk modeling, demand forecasting. | Converts historical data into actionable intelligence, enabling proactive strategy. |
E-Procurement Platforms | Provides a centralized system for the entire procure-to-pay process. | Managing requisitions, approvals, POs, and invoices in one place. | Establishes a single source of truth, enhancing visibility and control over spend. |
Supplier Portals | Offers suppliers a self-service interface for transactions and communication. | Invoice submission, payment status tracking, updating company info. | Reduces AP workload, improves data accuracy, and strengthens supplier relationships. |
While each technology serves a distinct purpose, their true power is realized through integration, creating an intelligent system greater than the sum of its parts. This is the foundation of AI MVP development for internal procurement tools.
The Core Automation Engines
At the foundational level, Robotic Process Automation (RPA) serves as the engine for transactional efficiency. RPA bots are digital workers programmed to execute high-volume, rules-based tasks—such as extracting data from invoices and entering it into an ERP system—with perfect accuracy, 24/7.
However, RPA executes predefined scripts; it does not learn or adapt. This is where Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) introduce cognitive capabilities, elevating automation from task execution to intelligent decision-making. To achieve truly smart procurement, organizations must leverage Intelligent Process Automation software.
AI and ML algorithms excel at analyzing vast datasets to identify non-obvious patterns, predict future demand, assess supplier risk, and recommend optimal sourcing strategies. Historical spend data is transformed from a static record into a predictive strategic asset.
For instance, an ML model can analyze historical purchasing data against real-time market signals to forecast a potential shortage of a critical component, enabling proactive inventory management. This represents a strategic shift from a reactive to a predictive procurement posture. Our guide on AI integration provides a technical roadmap for embedding this intelligence into existing systems.
Creating a Unified Ecosystem
These intelligent engines operate within unified platforms that create a seamless, end-to-end procurement environment. Two critical components of this ecosystem are:
E-Procurement Platforms: These act as the central nervous system for the entire procure-to-pay cycle, managing all activities from requisition to payment. They provide a single, authoritative view of all procurement operations.
Supplier Portals: These platforms are pivotal for optimizing supplier relationships. They replace inefficient email and phone communication with a self-service portal for invoice submission and payment tracking, significantly reducing the administrative burden on accounts payable and fostering trust through transparency.
Unlocking Measurable Business Outcomes
Implementing automation in procurement is not a technology exercise; it is a strategic initiative designed to generate tangible, measurable value that directly impacts financial performance and operational resilience.
The most immediate and quantifiable outcome is a significant reduction in operational costs. Automating tasks like purchase order creation and invoice matching eliminates thousands of hours of manual data entry. This frees skilled professionals from administrative work to focus on high-impact strategic activities, such as negotiating favorable terms and conducting deep spend analysis to identify new savings opportunities.
Driving Efficiency and Resilience
Beyond direct cost savings, the gains in operational efficiency are profound. Automation accelerates the entire procure-to-pay lifecycle, reducing cycle times and eliminating the bottlenecks that delay critical purchases. This translates to faster approvals, timely payments, and streamlined supplier onboarding, resulting in a more agile operation capable of responding to market dynamics.
The empirical data is compelling. Industry reports indicate that automation can drive a 25% improvement in overall efficiency and eliminate up to 60% of manual tasks. Leading organizations are on a trajectory to realize savings of $550 million by 2025 through these initiatives.
In an environment where 78% of Chief Procurement Officers perceive increasing market volatility, the 52% of teams leveraging automation are gaining a distinct competitive advantage. The ability of automated approval workflows to shorten procurement cycles by up to 50% is a key enabler of this agility.
Enhancing Strategic Capabilities
The benefits extend beyond efficiency and cost reduction to unlock powerful strategic advantages that fortify the entire enterprise.
Complete Spend Visibility: Centralized data and automated reporting provide a granular, real-time view of every dollar spent, eliminating rogue purchasing and enabling sophisticated budget management.
Stronger Supplier Partnerships: Consistent, on-time payments and transparent communication build trust, forming the bedrock of strategic partnerships that yield better terms, innovation, and supply chain resilience. Automation is a core component of effective vendor management strategies.
Ironclad Compliance: An automated system acts as a diligent policy enforcement engine, ensuring every transaction adheres to internal controls and external regulations. This dramatically reduces risk and creates an unimpeachable audit trail.
These benefits are synergistic. For a deeper analysis of their interplay, review our guide on the strategic benefits of AI business automation. Together, they elevate procurement from a tactical, back-office function to a strategic driver of corporate resilience and profitability.
Your Step-By-Step Implementation Roadmap
Transitioning to an automated procurement ecosystem is a strategic transformation, not a simple software installation. A methodical, phased implementation is critical to maximizing ROI while minimizing operational disruption. This four-stage roadmap provides a structured approach from initial analysis to enterprise-wide adoption.
Phase 1: Assess and Identify Opportunities
Before implementing any technology, a comprehensive analysis of the current state is essential. Map the entire procure-to-pay (P2P) lifecycle, from initial requisition to final supplier payment, to identify process bottlenecks, redundancies, and high-friction activities.
Focus on high-volume, repetitive tasks that consume significant manual effort. These represent prime candidates for initial automation and quick wins. Common areas include:
Invoice Processing: Manual data entry from PDF invoices into the ERP system.
Purchase Order Creation: Generation of standard POs for routine, recurring purchases.
Approval Workflows: Management of complex, multi-stage approval chains via email.
Quantify the pain points. Calculate the man-hours per week dedicated to these tasks and the associated error rates. This data is foundational for building a compelling business case for investment.
Phase 2: Select the Right Technology Stack
With a clear understanding of your requirements, the next step is technology selection. The market offers a wide array of solutions; let your specific process needs and integration requirements—not just a vendor's feature list: guide your decision. Prioritize solutions that offer robust, pre-built integrations with your existing Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) and financial systems.
A critical failure point is selecting a technologically superior tool that suffers from poor user adoption. Prioritize user experience (UX) and the platform's ability to scale. A solution that is difficult for your team to use will create more friction than it removes.
Conduct a focused pilot program with a shortlist of vendors. This allows you to evaluate usability, assess the complexity of integration, and gauge the quality of vendor support in a controlled, real-world environment. A great way to test a platform is by building a simple workflow; check out our beginner's guide to building your first automation for a practical example of how this works: https://magic.app/blog/n8n-complete-beginner-s-guide-to-building-your-first-automation
Phase 3: Integrate and Launch a Pilot Program
This phase involves the core technical implementation. The selected automation platform must integrate seamlessly with your core business systems to ensure data integrity and fluid process handoffs. This requires close collaboration between IT, procurement, and the software vendor to define data mappings and configure robust APIs.
Once integrated, launch a targeted pilot program. Select one of the high-impact processes identified in Phase 1, such as automated three-way invoice matching. A successful pilot accomplishes three critical objectives:
Proves the Concept: Delivers tangible ROI and efficiency gains to build stakeholder confidence.
Gathers Feedback: Collects user input to refine workflows before a full-scale rollout.
Builds Momentum: Creates internal champions who will advocate for broader adoption.
This diagram illustrates the direct correlation between automation initiatives and key business outcomes.
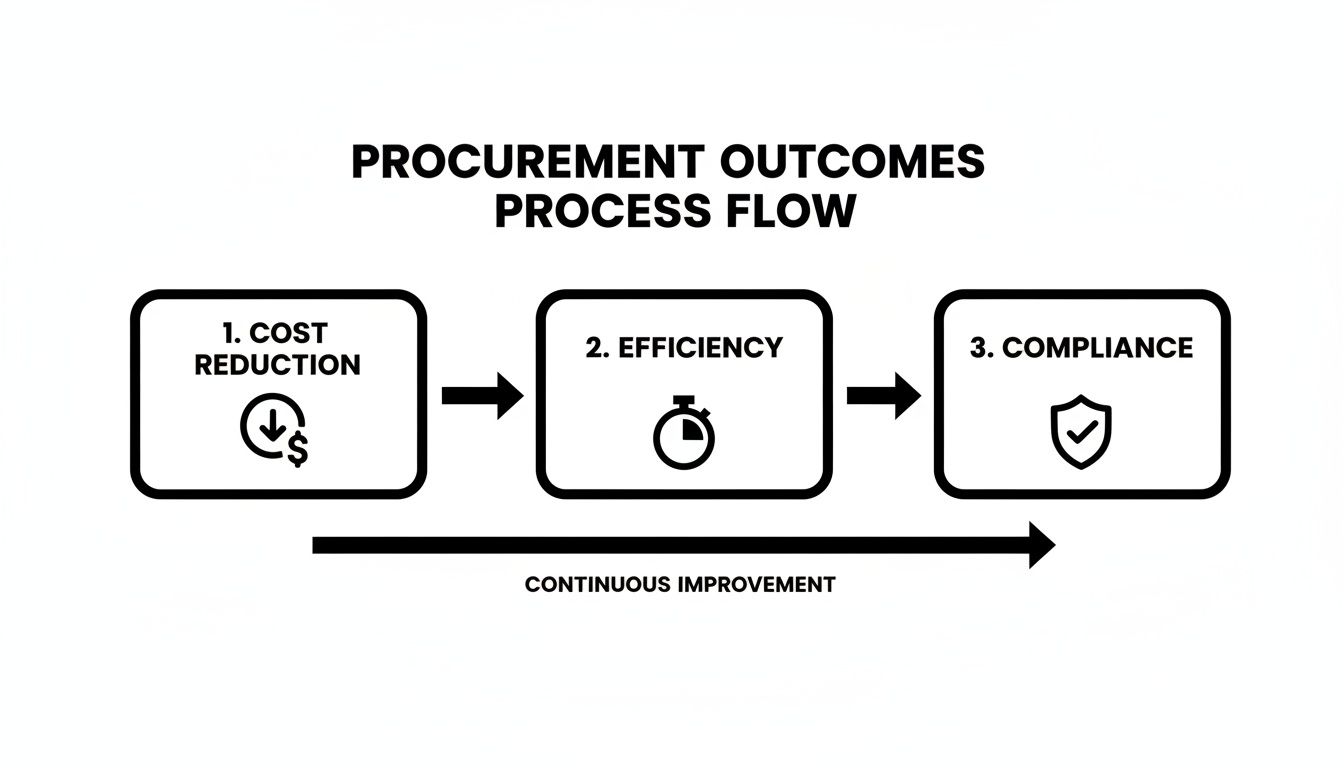
Every step in your implementation plan must be clearly linked to driving cost reduction, efficiency gains, or enhanced compliance.
Phase 4: Drive Change and Empower Your Team
Technology is only one component of a successful transformation; the human element is paramount. Without a deliberate change management strategy, even the most sophisticated software will fail to deliver its promised value. Clearly articulate the strategic "why" behind the shift, emphasizing how automation eliminates tedious work to free up personnel for higher-value, more engaging tasks.
Provide comprehensive training and establish accessible, ongoing support channels. Develop a knowledge base with tutorials and best practices. Crucially, invest in upskilling your team to develop the analytical and strategic competencies required in an automated environment. When automation is positioned as an enabler of human potential, not a replacement, you secure the buy-in necessary for long-term success.
How to Measure Success and Overcome Hurdles
Deploying a procurement automation system is the beginning, not the end, of the journey. The subsequent challenge is to rigorously measure its impact, demonstrate ROI, and navigate the inevitable implementation hurdles. Success is defined not just by process acceleration but by a robust, data-driven validation of the strategic investment.
First, move beyond anecdotal wins. Establish a clear framework of Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) to objectively measure performance. A well-designed KPI dashboard is more than a reporting tool; it is a strategic instrument for communicating value to leadership and identifying opportunities for continuous improvement.
Defining Your Key Performance Indicators
To gain a holistic view of automation's impact, track metrics across three core domains: efficiency, cost, and compliance. This multi-faceted approach provides a comprehensive performance picture and pinpoints areas for further optimization.
Efficiency Metrics: Monitor the requisition-to-order cycle time. This measures the velocity of your procurement process from request to execution. A significant reduction directly benefits business agility. Also, track invoice processing time as a key indicator of back-office operational health.
Cost Metrics: Go beyond simple cost-cutting. Measure cost avoidance (savings realized through strategic sourcing and negotiation enabled by better data) and the percentage of spend under management. The objective is to channel the maximum possible organizational spend through the controlled, automated system.
Compliance and Risk Metrics: The maverick spend rate is a critical indicator of user adoption and policy adherence. It quantifies the percentage of spend occurring outside of approved channels. Additionally, track supplier compliance rates to ensure adherence to negotiated contract terms.
A well-defined set of KPIs is essential for demonstrating the value of your automation project.
KPIs for Measuring Procurement Automation ROI
Metric Category | Specific KPI | Description | Benchmark Goal |
|---|---|---|---|
Process Efficiency | Requisition-to-Order Cycle Time | The average time from when a purchase request is created until a purchase order is issued to the supplier. | Reduce by 30-50% |
Cost Savings | Percentage of Spend Under Management | The proportion of total company spend that is actively managed by the procurement department through approved channels. | Increase to over 85% |
Compliance | Maverick Spend Rate | The percentage of spending that occurs outside of negotiated contracts and approved procurement processes. | Decrease to under 10% |
Supplier Performance | On-Time Delivery Rate | The percentage of orders delivered by the supplier on or before the agreed-upon delivery date. | Maintain above 95% |
By consistently monitoring these KPIs, you can create a clear narrative around the success of your initiatives and identify opportunities for further optimization.
Navigating Common Implementation Challenges
Even meticulously planned automation projects encounter obstacles. Proactively identifying and addressing these potential failure points is key to maintaining project momentum.
The most common points of failure in automation projects are not technological but organizational: resistance to change and poor data hygiene. Without a foundation of clean data and a team that embraces new tools, even the most powerful platform will underperform.
Let's examine the three most prevalent challenges and strategies to mitigate them.
1. Poor Data Quality
Automation systems are only as effective as the data they process. If master data—supplier information, contract terms, product catalogs—is inaccurate or inconsistent, the system will simply automate errors at scale.
This requires a preemptive data governance strategy. Initiate a data cleansing project before implementation. Establish and enforce strict data entry standards and assign clear ownership for data maintenance moving forward.
2. Resistance to Change
The term "automation" often triggers employee anxiety about job displacement. This resistance can sabotage user adoption.
Address this fear proactively and transparently. Frame the technology as a tool for augmenting human capabilities, not replacing them. The core message should be one of empowerment: automation eliminates mundane tasks, allowing the team to focus on strategic work that requires human intellect and negotiation skills, such as complex sourcing and supplier relationship management.
3. Complex Integrations
Integrating a new procurement platform with legacy ERP and accounting systems is often the most significant technical challenge.
Mitigate this risk by making integration capabilities a primary criterion in your technology selection process. Prioritize platforms with pre-built connectors and robust, well-documented APIs. Crucially, involve your IT team from the outset of the evaluation process. Map all required integration points and data flows before signing any contracts to prevent unforeseen technical debt and project delays.
Common Questions About Procurement Automation
As you consider an automation initiative, strategic and practical questions will naturally arise. Addressing these is critical for building stakeholder confidence and formulating a sound implementation strategy. Here are our answers to the most common inquiries.
What Is the Typical ROI for Procurement Automation?
The return on investment extends far beyond direct cost savings, although these are significant. Most organizations realize a hard ROI of 3-8 times their initial investment within 18 months. However, the full value proposition includes substantial indirect benefits.
Immediate financial gains are typically derived from:
Lower Process Costs: The cost per invoice or purchase order can be reduced by 50% or more.
Increased Spend Under Management: Bringing maverick spend under control enables organizations to leverage volume discounts and negotiate more favorable terms.
The long-term strategic value, however, is often more impactful. This includes enhanced risk mitigation through systematic supplier vetting, stronger supplier relationships fostered by reliable on-time payments, and bulletproof compliance that avoids costly fines and penalties.
Where Should We Start with a Limited Budget?
With constrained resources, a phased approach focused on a high-impact "quick win" is the most prudent strategy. Avoid attempting a "big bang" implementation. Instead, target a high-volume, low-complexity process that is a major source of administrative friction.
The classic starting point is automated invoice processing. This process is well-defined and delivers clear, measurable outcomes: reduced error rates, accelerated cycle times, and lower processing costs. A successful pilot in this area provides the empirical data required to build a compelling business case for a broader procure-to-pay transformation.
This initial success builds critical momentum and stakeholder buy-in, making it easier to secure funding for more ambitious phases of your automation roadmap.
Will Automation Replace Our Procurement Team?
This is the most frequent—and understandable—concern. The definitive answer is no. Automation does not replace procurement professionals; it elevates their role. These tools are designed to handle the repetitive, low-value tasks that consume a skilled professional's time.
By automating routine work, you empower your team to concentrate on high-value activities that require human judgment, creativity, and interpersonal skills. This means dedicating more time to complex contract negotiations, strategic sourcing, fostering supplier innovation, and navigating supply chain risk—functions that algorithms cannot perform. Automation in procurement is a powerful tool for augmenting human talent, not rendering it obsolete.
Are you an entrepreneur or VC looking to accelerate your go-to-market strategy? Magic specializes in AI MVP development and AI startup services, turning visionary concepts into market-ready products. We build AI prototypes for VCs to validate opportunities and provide AI product acceleration for founders. Let’s discuss how we can de-risk your investment and fast-track your success. Contact us.




