Product Market Fit Validation: An Analytical Framework for AI-Powered MVPs
MVP
14 mins
Dec 12, 2025

Khyati Mehra
Product-market fit (PMF) is not a startup buzzword; it's the singular inflection point where a compelling technology evolves into a sustainable business. For an AI venture, achieving PMF signifies that your product doesn’t just occupy a market—it fundamentally satisfies a high-value demand within it. This guide provides a rigorous, analytical framework for navigating the path to product market fit validation, focusing on the unique challenges and opportunities of building AI-powered MVPs.
Beyond the Buzzword: A Strategic Framework for PMF
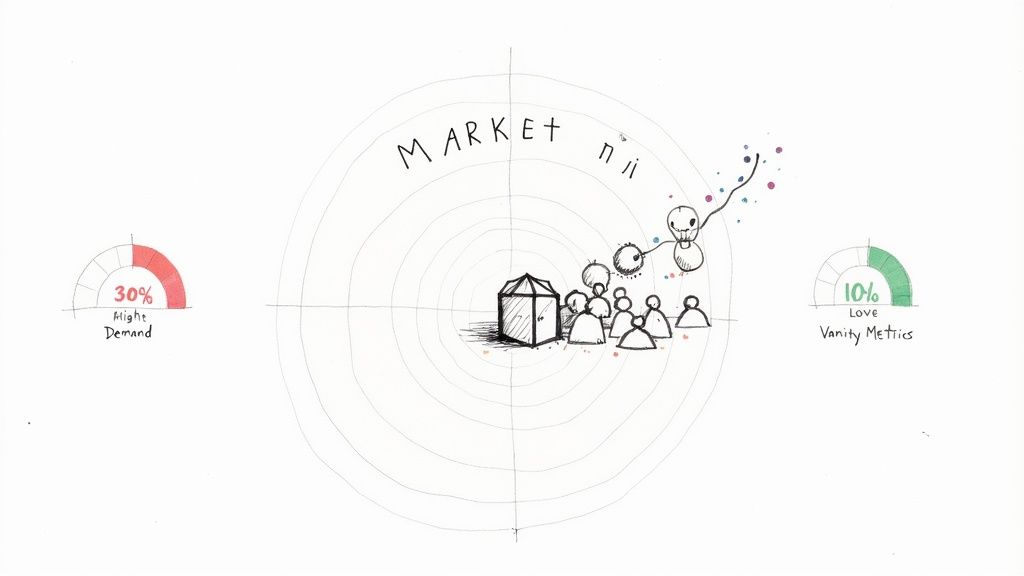

Many promising AI MVPs fail, and the post-mortem rarely reveals a technological deficit. The failure is almost always a market disconnect. Industry data consistently shows that a "lack of market need" is the primary cause of startup failure, accounting for over 35% of all collapses according to CB Insights. This underscores a critical truth: a brilliant algorithm or a sophisticated language model holds zero commercial value if its absence isn't felt by a target market.
When true PMF is achieved, you feel an organic pull from the market. Your product is not pushed; it is demanded. Key indicators include:
Accelerating, word-of-mouth-driven customer acquisition.
Shortening sales cycles as the value proposition becomes self-evident.
High user retention and strong organic engagement.
The Dangers of Vanity Metrics
Early-stage ventures are particularly susceptible to the allure of vanity metrics, superficial data points that create a false sense of progress while masking fundamental flaws in the value proposition. Distinguishing between actionable signals and misleading noise is the core discipline of product market fit validation.
Vanity Metric: A surge in free trial sign-ups after a marketing campaign.
Actionable Metric: A high trial-to-paid conversion rate coupled with low monthly churn, indicating perceived value.
Vanity Metric: Positive social media mentions from a broad audience.
Actionable Metric: A high Net Promoter Score (NPS) from your ideal customer profile (ICP), with "Promoters" actively driving referrals.
This guide is engineered to provide an analytical framework to de-risk your AI venture. Before committing significant capital to complex AI prototypes for VCs or scaling your engineering team, you must validate your foundational assumptions with empirical rigor. Our AI MVP development process transforms PMF from a vague aspiration into a measurable, strategic discipline rooted in evidence-based iteration.
The journey to product-market fit is a process of building progressively stronger layers of market validation. An MVP is a critical experiment, but its success is predicated on a deep, data-backed understanding of the problem and the specific user cohort you are serving.
Our AI product acceleration philosophy centers on lean, rapid experimentation designed to generate high-fidelity market signals efficiently. This methodical approach is the core of our AI startup services. By treating validation as your core strategy, you sidestep the common traps that doom even the most technologically advanced products. To establish a strong foundation, review our guide on how to validate your startup idea for initial research and hypothesis testing.
Building Your Problem and Solution Hypothesis
Before a single line of code is written or a model is trained, the validation journey begins with a razor-sharp, falsifiable hypothesis. An ambiguous problem-solution framework is the fastest path to depleting capital and engineering resources. Over a third of startups fail because they build solutions for non-existent or low-intensity problems.
This initial phase is not about building; it's about articulating the acute pain point you are solving and for whom. A robust hypothesis acts as a strategic North Star, guiding every decision during your AI MVP development sprint and grounding your assumptions in market reality, not technological novelty.
Articulating the Core Problem
The first step is to transcend a vague concept and define the specific, high-stakes problem your ideal customer faces. This requires deep market intelligence and empathy, not just intuition. Your problem statement must diagnose the root cause of the pain, not merely describe its symptoms.
A powerful problem statement is measurable and emotionally resonant. It should quantify the real-world consequences of inaction—lost revenue, operational inefficiency, compliance risk, or competitive disadvantage. This clarity is invaluable for internal alignment and investor communication. A precise Ideal Customer Profile (ICP) is non-negotiable. Targeting "small businesses" is ineffective. A strategic ICP is specific: "Series A B2B SaaS companies with 50-100 employees experiencing high customer support ticket volume, leading to an average response time of over 24 hours."
A common failure pattern is founder attachment to a solution—particularly a sophisticated AI model—before rigorously defining the problem. A problem-first, solution-second discipline ensures you build a product that commands a budget.
Crafting a Testable Solution Hypothesis
With a clearly defined problem, you can formulate your solution hypothesis. This is not a feature list; it is a concise statement connecting your unique value proposition directly to the identified pain point. Crucially, your solution hypothesis must be falsifiable—you must be able to design an experiment that can prove it right or wrong. This scientific mindset is the essence of effective product market fit validation.
A robust hypothesis framework:
For [Your Ideal Customer Profile]
Who are struggling with [The specific, high-stakes problem]
Our AI solution provides [Your unique value proposition]
Unlike [Existing alternatives or competitors]
We deliver [A key, quantifiable outcome]
This structure forces specificity regarding your audience, their pain, your differentiation, and the tangible results you promise. It converts a pitch into a testable blueprint for your AI product acceleration strategy.
From Hypothesis to Actionable Insights
Let's operationalize this with a case study of an AI startup targeting marketing teams.
Weak Hypothesis: "Our AI will help marketers create better content."
This statement is untestable. It lacks a defined customer, a specific problem, and a measurable definition of "better."
Strong Hypothesis: "For B2B SaaS marketing managers at mid-stage startups (ICP) who struggle to scale personalized email campaign creation (Problem), our generative AI platform (Solution) provides hyper-segmented copy variants in seconds (Value Prop). Unlike hiring more copywriters or using generic templates (Alternatives), we increase email open rates by over 15% while reducing content creation time by 90% (Outcome)."
This hypothesis is specific, measurable, and directly informs the MVP's required functionality and success metrics. It provides a clear roadmap for targeted validation experiments. As you refine your own approach, explore different models to see what fits; learn more from The AI Founder's Guide to Minimum Viable Product Examples. A well-crafted hypothesis de-risks the entire development process, ensuring our AI startup services are focused on building products with intrinsic market pull from day one.
How to Design Lean Validation Experiments
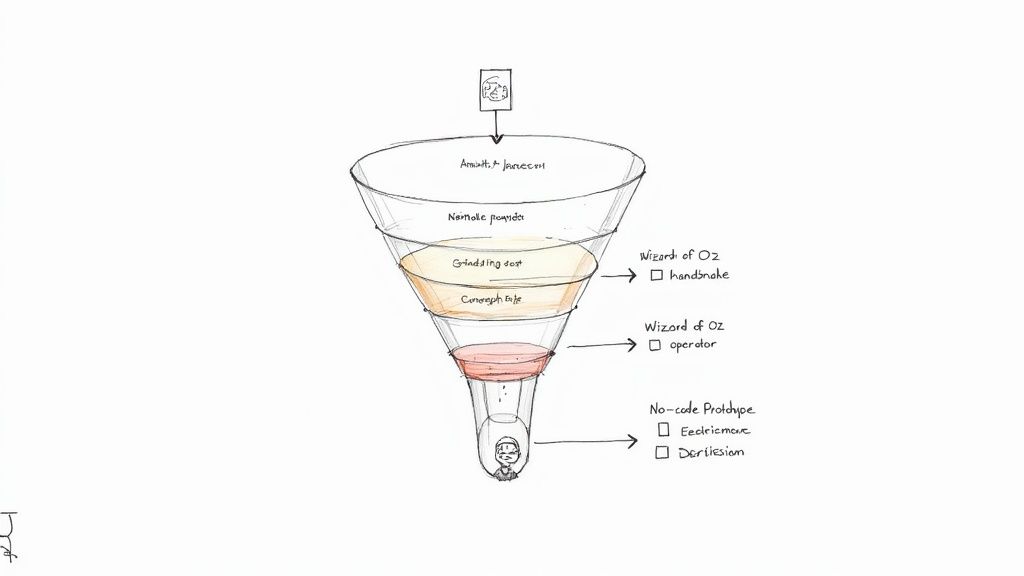
With a validated hypothesis, the next phase involves designing lean, capital-efficient experiments to generate the strongest possible market signal. For an AI startup, this means resisting the premature urge to build complex systems. The objective is not a polished product; it is actionable, real-world data acquired rapidly.
This phased approach to product market fit validation is your primary defense against building a solution nobody wants. The statistics are stark: a 2019 study by Nielsen found that 95% of new products fail. Smart, evidence-based validation is how you engineer your way into the top 5%.
Gauging Intent with Smoke Tests and Landing Pages
Before prototyping, a smoke test is your simplest, most effective initial experiment. This involves creating a marketing facade—typically a high-fidelity landing page—that presents your AI solution as if it were fully operational. The objective is to measure purchase intent, not just casual interest.
A strategic landing page articulates the value proposition from your hypothesis, showcases UI/UX mockups, and features a high-commitment call to action. Avoid a passive "learn more." Instead, solicit sign-ups for a closed beta or even pre-orders. The conversion rate on this action provides a potent, quantitative early signal of market demand before committing to intensive AI MVP development.
Simulating the AI Experience Manually
Once initial interest is confirmed, the next step is to validate the core value proposition without building the complex AI backend. Manual simulation MVPs are invaluable for this purpose. You deliver the promised outcome to early users, but with human experts performing the tasks the AI will eventually automate.
Two primary methodologies exist:
Concierge MVP: The user is fully aware that a human is delivering the service manually. This high-touch model is exceptional for gathering deep qualitative feedback and mapping the user's workflow intricacies.
Wizard of Oz MVP: The user believes they are interacting with a fully automated AI system, while your team manually executes the tasks behind the scenes. This is ideal for testing the usability and perceived value of the AI interaction itself. It answers critical questions like, "Is the AI's output genuinely useful?" and "Does this automated workflow solve the core problem effectively?"
Both are foundational tactics for lean AI product acceleration, allowing you to iterate on the solution's value before investing heavily in model development. This is a critical component of product design, which we explore further in our guide on how usability testing drives product growth.
A Wizard of Oz MVP forces a direct confrontation with your idea's raw utility. If users fail to find value when a team of experts manually delivers the perfect output, a complex algorithm will not salvage a flawed value proposition.
Each experiment type has a strategic place depending on your learning objectives and available resources.
Building Functional No-Code AI Prototypes
For a more tangible asset to engage early adopters or present to investors, functional prototypes built with no-code platforms are highly effective. Tools like Bubble, Webflow, and WeWeb can be integrated with commercial AI APIs from providers like OpenAI or Anthropic. This approach yields surprisingly sophisticated AI prototypes for VCs at a fraction of the time and cost of traditional development.
These prototypes are not built for scale. Their purpose is to credibly demonstrate the core user journey and deliver the "magic" AI-powered moment. This is the optimal path for testing specific workflows, gathering usability feedback, and securing initial investment. When providing AI startup services, this is a frequently recommended strategy for creating a demonstrable asset that aligns all stakeholders.
The key is to structure this work into focused sprints, each with a clear learning objective and a defined go/no-go decision metric. Every experiment must yield actionable data that moves you quantifiably closer to product-market fit.
Measuring What Matters for PMF Validation
Investor confidence is secured with data, not just narrative. While early experiments provide directional validation, the discipline of product market fit validation hinges on measuring the metrics that truly signify market traction. It is critical to avoid the distraction of vanity metrics that signal activity without proving user dependency.
To go beyond surface-level data, focus on metrics that demonstrate user activation, retention, and engagement. These are the vital signs of your AI startup’s health and the leading indicators of PMF.
The Litmus Test: The 40% Rule
The most direct method for measuring "must-have" status is the benchmark developed by Sean Ellis. The methodology is simple: survey your users and ask, "How would you feel if you could no longer use this product?"
If at least 40% of respondents answer that they would be "very disappointed," you have a powerful signal of product-market fit. This threshold was derived from analyzing hundreds of startups, correlating this response with the ability to build high-growth, sustainable businesses. You can explore how to apply this data-driven approach on mixpanel.com.
This single question cuts through the noise to deliver a clear verdict on whether your product has become indispensable to a meaningful segment of your user base. This is the hard evidence that validates your market position and informs your strategy for AI product acceleration.
Is your current analytics setup providing this level of clarity? If not, it may be time for a strategic re-evaluation. Explore our AI MVP consulting services to build a data-driven validation framework that delivers the insights investors demand.
Making the Go No-Go Decision
You have executed experiments and aggregated data. However, data collection is only the precursor to the real test of leadership: making a clear, evidence-backed decision. This is the moment of truth in your product market fit validation journey—a conscious choice to scale, pivot, or terminate.
Here, you must synthesize your quantitative metrics with your qualitative insights. The numbers tell you what is happening; user interviews explain why. This combined analysis provides a high-resolution view of your market position, free from cognitive biases like confirmation bias or sunk cost fallacy.
Interpreting Strong PMF Signals
True product-market fit is not subtle; it is a powerful force. The market begins to pull the product from you. These are the definitive green lights to scale your AI MVP development and increase investment.
Key indicators of strong PMF include:
Effortless Organic Growth: Your user base expands through word-of-mouth, with users becoming brand evangelists. Your Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) should be low and trending downward.
High User Retention: Retention cohort curves flatten, demonstrating that a core segment of users has integrated your product into their routine operations.
Accelerating Sales Cycles: For B2B products, prospects understand the value proposition with minimal friction. Objections decrease, and deal velocity increases because the ROI is self-evident.
When you achieve PMF, the dynamic inverts. You shift from pushing a product onto a market to managing the inbound demand the market generates. Your primary challenge evolves from customer acquisition to customer success and infrastructure scaling.
Recognizing the Red Flags to Pivot or Persevere
Equally critical is the ability to recognize negative signals. Ignoring these red flags is a common and costly error. These indicators demand a rigorous re-evaluation of your core hypothesis and often necessitate a strategic pivot.
Look beyond vanity metrics. The retention rate is your most critical measure of product stickiness. For a consumer SaaS product, a 30-day retention rate below 30% is a significant concern. A high churn rate is an unambiguous signal that your product fails to deliver on its promise. For more on this, see the analysis on leveraging key metrics for PMF on wednesday is.
This decision tree provides a simple framework for interpreting your PMF metrics and guiding your next strategic move.

As the diagram illustrates, falling short of the '40% Rule' threshold is a strong indicator that your current value proposition lacks the necessary intensity to build a loyal, paying user base.
An Objective Decision Framework
Emotion is the enemy of sound strategic decision-making at this stage. Employ a structured framework, like a go/no-go checklist, to ensure objectivity.
Go/Scale Checklist:
Retention: Does your cohort retention curve flatten at a rate that supports a viable business model?
The 40% Rule: Do more than 40% of surveyed users report they would be "very disappointed" if they could no longer use your product?
Activation: Is your activation rate—the percentage of users who experience the "aha!" moment—consistently high and stable or improving?
Organic Demand: Are new users discovering you through word-of-mouth, and is your CAC sustainably low?
If you cannot confidently affirm these points, the correct action is not to increase marketing spend but to pivot your strategy. Making these high-stakes decisions is challenging. Our AI startup services provide the analytical rigor and external perspective to interpret your data accurately. Let's discuss how our AI product acceleration program can bring clarity to your go-to-market strategy.
Got Questions About Nailing Product-Market Fit? We’ve Got Answers.
The path to product-market fit, particularly for AI ventures, is complex. Founders and investors consistently grapple with fundamental questions regarding timelines, execution risks, and signal interpretation. Here, we address the most pressing inquiries.
How Long Should This Actually Take for an AI Startup?
There is no fixed timeline. The product-market fit validation process is measured in learning cycles, not calendar months. For most AI startups, this phase typically ranges from three to nine months, contingent on product complexity and market velocity. The critical variable is the speed at which you can execute build-measure-learn loops.
An enterprise-grade, workflow-integrated AI B2B SaaS tool will inherently require a longer validation runway to account for sales cycles and cohort analysis. Conversely, a consumer-facing generative AI application might achieve signal clarity much faster through high-volume A/B testing.
The objective is not to race to a predetermined launch date. The objective is to de-risk your core assumptions as rapidly and cheaply as possible. A six-month validation process that informs a critical pivot is infinitely more valuable than a three-month process that validates a flawed strategy.
Structure your timeline around learning milestones. Focus on accelerating the cadence of your experiments—from landing pages to functional AI prototypes for VCs—to shorten the path to a conclusive, data-backed answer.
What are the Most Common Ways Founders Mess This Up?
Founder optimism is a powerful asset, but it can lead to critical errors in judgment during validation. The two most common and capital-intensive mistakes are misinterpreting market signals and scaling prematurely.
Key pitfalls to avoid:
Mistaking Politeness for Purchase Intent: Early feedback from personal or professional networks is often positively biased. Vague praise like "this is cool" is not a buying signal. Validation requires evidence of a burning need, proven either by a willingness to pay or deep, habitual usage.
Premature Scaling: Investing heavily in marketing before achieving a flat retention curve is akin to filling a leaky bucket. It creates the illusion of growth while masking a core product deficiency, leading to high churn and inefficient capital burn.
Ignoring the "Why" Behind the Numbers: Quantitative data reveals what is happening; qualitative feedback explains why. Dismissing the user stories behind high churn or low activation rates is a path to building a product nobody loves.
Over-Engineering the MVP: This is the cardinal sin of AI MVP development. Do not invest months building a complex AI backend before validating the core value proposition. A failed Wizard of Oz test is an inexpensive lesson; a failed, fully engineered product is a catastrophic one.
Can You Really Find PMF with Just a Handful of Users?
Absolutely. For many B2B AI startups, it is the only viable path. Product-market fit is not defined by user volume but by the intensity of user need within a specific market segment.
Prioritize depth over breadth. A cohort of 20-30 paying customers who would be "very disappointed" if your product disappeared, exhibit high retention, and actively refer new business is a far stronger PMF signal than 5,000 free users with low engagement and no brand loyalty.
This is especially true for enterprise AI solutions where the target market is inherently small but the contract value is high. Demonstrating rock-solid engagement and retention within a tightly defined Ideal Customer Profile (ICP) is the definitive proof required to justify an AI product acceleration strategy.
Navigating the validation process can be daunting. The road to product-market fit is challenging, but you don't have to travel it alone. Magic specializes in design-first AI MVP development, helping founders transform ambitious ideas into market-validated products with speed and precision.
Are you prepared to build an AI product with validated market demand? Download our exclusive 'AI MVP Validation Checklist' to ensure your strategy is built on a foundation of data, not assumptions.
Explore our AI startup services and build your MVP the right way.




